原地哈希
1164字约4分钟
2024-10-20
前言
原地哈希
算法概要
原地哈希算法,可以将其拆分为两个关键字:原地和哈希。
所谓原地很好理解,就是指空间复杂度为 O(1),而哈希在这里与题目有着密切的关系,存在明确的哈希映射关系。
我们举个例子,数据范围 在 [1, n] 的长度为 n 的数组,所有的数都不相同,要求在 O(n) 时间复杂度内完成排序。
一般排序是基于元素值的大小来决定顺序的,即元素值决定了排序后的位置,而对于上面这种条件,不妨让 nums[i] 就放到索引为 nums[i] - 1 的位置。
所以这里明确的哈希关系就是 f(x) = x - 1
而对每个数组中的每个元素在原地进行哈希运算之后,就可以将每个数都归为到正确的位置。
比如:序列为 [2, 7, 6, 4, 3, 5, 8, 1]
那么使用原地哈希的思想,整个数组就可以被置换环分割。
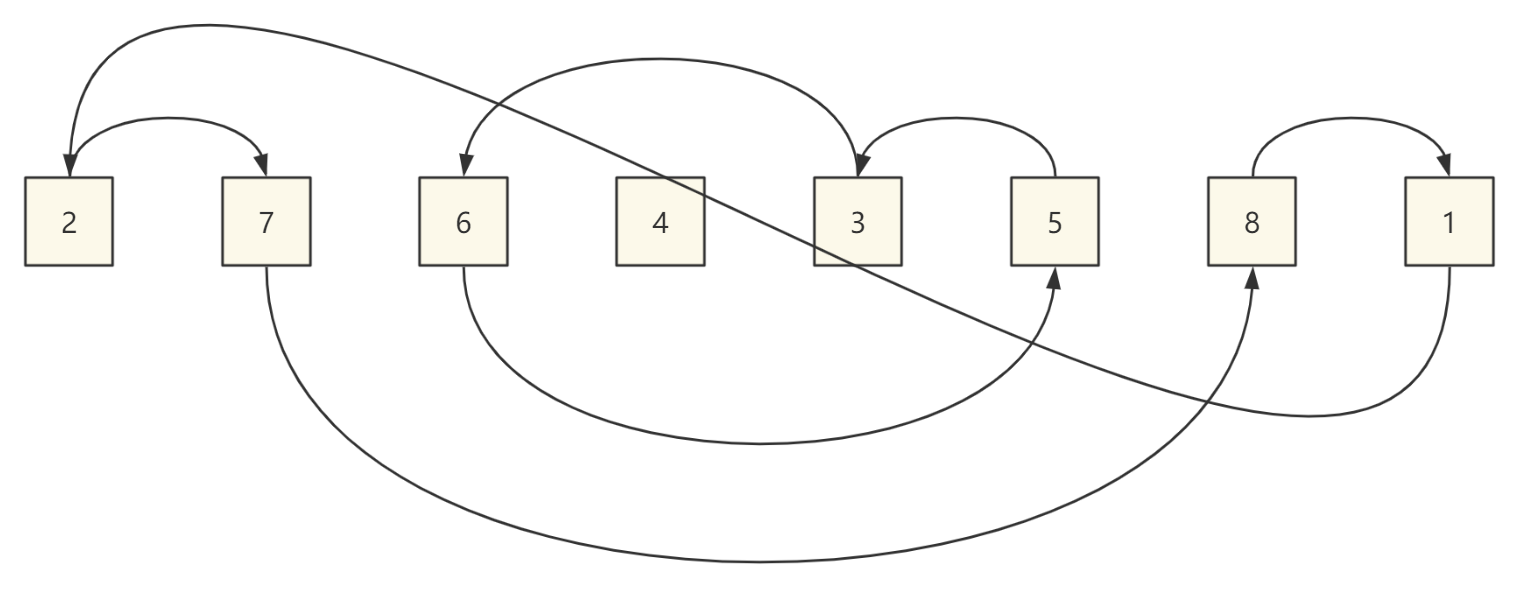
如上图所示,整个序列被三个置换环分割,2、7、8、1、2,6、5、3、6,4、4。
public void sort(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while (hash(nums[i]) != i) {
// 不断交换
swap(nums, i, hash(nums[i]));
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
}
public int hash(int x) {
return x - 1;
}
public void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}下面我们来分析一下时间复杂度,首先结论是 O(n)。
比较有讨论的点就在 while 循环部分,while 循环不会每一次都把数组里面的所有元素都看一遍,如果有一些元素在这一次的循环中被交换到了它们应该在的位置,那么在后续的遍历中,由于它们已经在正确的位置上,代码再执行到它们的时候,就会直接跳过。
最极端的一种情况是,在第 1 个位置经过这个 while 就把所有的元素都看了一遍,所有的元素都被正确的放置在它们应该在的位置,那么 for 循环后面的部分的 while 的循环体都不会被执行。
平均下来,每个数只需要看一次就可以了,while 循环体被执行很多次的情况不会每次都发生,这样的复杂度分析的方法叫做 均摊复杂度分析。
题目
缺失的第一个正数
class Solution {
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int h;
while ((h = hash(nums[i])) >= 0 && h < n && h != i && nums[h] != nums[i]) {
swap(nums, h, i);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (hash(nums[i]) != i) {
return i + 1;
}
}
return n + 1;
}
public int hash(int x) {
return x - 1;
}
public void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}寻找重复数
class Solution {
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int h;
while ((h = hash(nums[i])) >= 0 && h < n && h != i) {
if (nums[h] == nums[i]) {
return nums[h];
}
swap(nums, h, i);
}
}
return -1;
}
public int hash(int x) {
return x - 1;
}
public void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}数组中重复的数据
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDuplicates(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int h;
while ((h = hash(nums[i])) >= 0 && h < n && h != i && nums[h] != nums[i]) {
swap(nums, h, i);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (hash(nums[i]) != i) {
res.add(nums[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
public int hash(int x) {
return x - 1;
}
public void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}找到所有数组中消失的数字
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int h;
while ((h = hash(nums[i])) >= 0 && h < n && h != i && nums[h] != nums[i]) {
swap(nums, h, i);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (hash(nums[i]) != i) {
res.add(i + 1);
}
}
return res;
}
public int hash(int x) {
return x - 1;
}
public void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}寻找文件副本
class Solution {
public int findRepeatDocument(int[] documents) {
int n = documents.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int h;
while ((h = hash(documents[i])) >= 0 && h < n && h != i) {
if (documents[h] == documents[i]) {
return documents[i];
}
swap(documents, i, h);
}
}
return -1;
}
public int hash(int x) {
return x;
}
public void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}